Describe the Mechanism of Enzyme Activity
This active site is a specific area that combines with the substrate. In the protoplasm enzymes exist as hydrophilic colloids.

Spliceosome Molecular Biology Molecular Biology Molecular Biology
This occurs when the concentration of the product reaches certain levels.

. Fisher 1894 Suggested the Lock and Key hypothesis. The combination formed by an enzyme and its substrates is called the enzymesubstrate complex. Catalysis is observed in the mechanism of the chymotrypsin reaction.
Recall from Chapter 6 that there are six major classes of biochemical reactions that are mediated by enzymes Table 71. Feedback inhibition is a type of inhibition in which the end product of a chain reaction inhibits the fi. Binding of substrate in proper orientation up to 102-fold 3.
The product reaches and binds to the enzyme and brings conformational changes in it leading to inhibition of its catalytic functions. The combination formed by an enzyme and its substrates is called the enzymesubstrate complex. Enzyme activity speeds up chemical reactions through specific chemical mechanisms lowering the activation energy required for a reaction.
View the full answer. Describe the mechanism of enzyme action. The active site is the specific region of the enzyme which combines with the substrate.
Enzyme a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process. Nearly all enzymes are proteins although some catalytically active RNA molecules have been. Enzymes are usually much bigger than their substrates By oriented binding and immobilization of the substrate enzymes facilitate catalysis by four ways 1.
The cell has several mechanisms to regulate enzyme activity. Such enzymes have an allosteric site that is joined to a specific metabolite. Enzymes are biological catalysts also known as biocatalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms and which can be extracted from cells and then used to catalyse a wide range of commercially important processes.
Describe the mechanism of chymotrypsins action. An enzyme attracts substrates to its active site catalyzes the chemical reaction by which products are formed and then allows the products to dissociate separate from the enzyme surface. When the affected aa are involved in catalysis the activity of the enzyme is affected.
Inhibitor active groups compete with substrate active groups andor active groups at. A brief treatment of enzymes follows. Bring substrates close to catalytic residues 2.
Enzymes work best with a narrow pH range. The basic mechanism of enzyme action is to catalyze the chemical reactions which begins with the binding of the substrate with the active site of the enzyme. Properties and Mechanism of Enzyme Action 1.
The allosteric effector causes changes in the structure of the active center that reduce or increase the activity of the enzyme. The biological processes that occur within all living organisms are chemical reactions and most are regulated by enzymes. Explore this through analyzing two concepts.
It digests meat eggs seeds or dairy products and breaks them into peptides. ENZYMES ENHANCE THE RATE OF REACTION BY LOWERING FREE ENERGY OF ACTIVAION A chemical reaction S P where S is the substrate and P is the product or products will take place when a certain number of S molecules at any given instant posses enough energy to attain an activated condition called the transition state in which the probability of making or breaking a. Show the process from the viewpoint of the enzyme.
An enzyme attracts substrates to its active site catalyzes the chemical reaction by which products are formed and then allows the products to dissociate separate from the enzyme surface. This is a mechanism of enzyme inhibition where the product formed from the biochemical reaction inhibits the further enzyme action. Any variation above or below a specific level reduces their rate of activity.
The activity of many enzymes is regulated according to the allosteric principle. For full treatment see protein. Mechanism of enzyme function Functions of Enzymes.
BIVA AIXE E 3 1 1 E - GT 112pt Paragraph. Our mission is to provide an online platform to help students to share notes in Biology. The basic mechanism by which enzymes catalyze chemical reactions begins with the binding of the substrate or substrates to the active site on the enzyme.
Pepsin Trypsin Amylase Rennin etc. Stabilization of transition state by electrostatic interactions. Enzymes act catalysts are required in small amount highly specific act best at a temperature.
Pepsin is a very powerful enzyme and it digests proteins in the stomach. Question 1 Describe the mechanism of feedback inhibition and the role this role process plays in controlling enzyme activity. Lock and Key Theory Contemplate theory has.
Enzyme binds with substrate at active site in the form of a lock-k ey 3D arrangement for induced fit. Some enzymes exist in a cell as components of complexes containing a number of enzymes. These include oxidation-reduction reactions group transfer reactions hydrolysis reactions the formationremoval of carbon-carbon double bonds isomerization reactions and ligation reactions.
Introduction - Enzyme Characteristics. Anonymous Answered question January 5 2021. Koshland Induced Fit Theory.
Enzyme interacts with substrate in 11 ratio at active site to catalyze the reaction. This chapter covers the basic principles of enzymology such as classification structure kinetics and inhibition and. One mechanism is genetic regulation.
PH affects enzymatic rates The solution pH affects the ionization states of amino acids within proteins and enzymes just as it affects ionizable groups in free amino acids. The mechanism of enzymatic action. Just as the number of cars produced controls how.
The binding of the substrate to the enzyme causes changes in the distribution of. This website includes. How it catalysis the hydrolysis of certain amide bonds in proteins as its substrates show the catalytic triad.

Why Is Water A Polar Molecule Water Molecule Molecules Polarity Of Water

Induced Fit Model Of Enzyme Action Enzymes Chemical Changes Active Site

Mitochondria And Chloroplasts Worksheet Pdf Download Mitochondria Chemical Energy Worksheets

Why Do Root Hair Cells Not Have Chloroplasts Biology Quiz Plant Cell Organelles Root
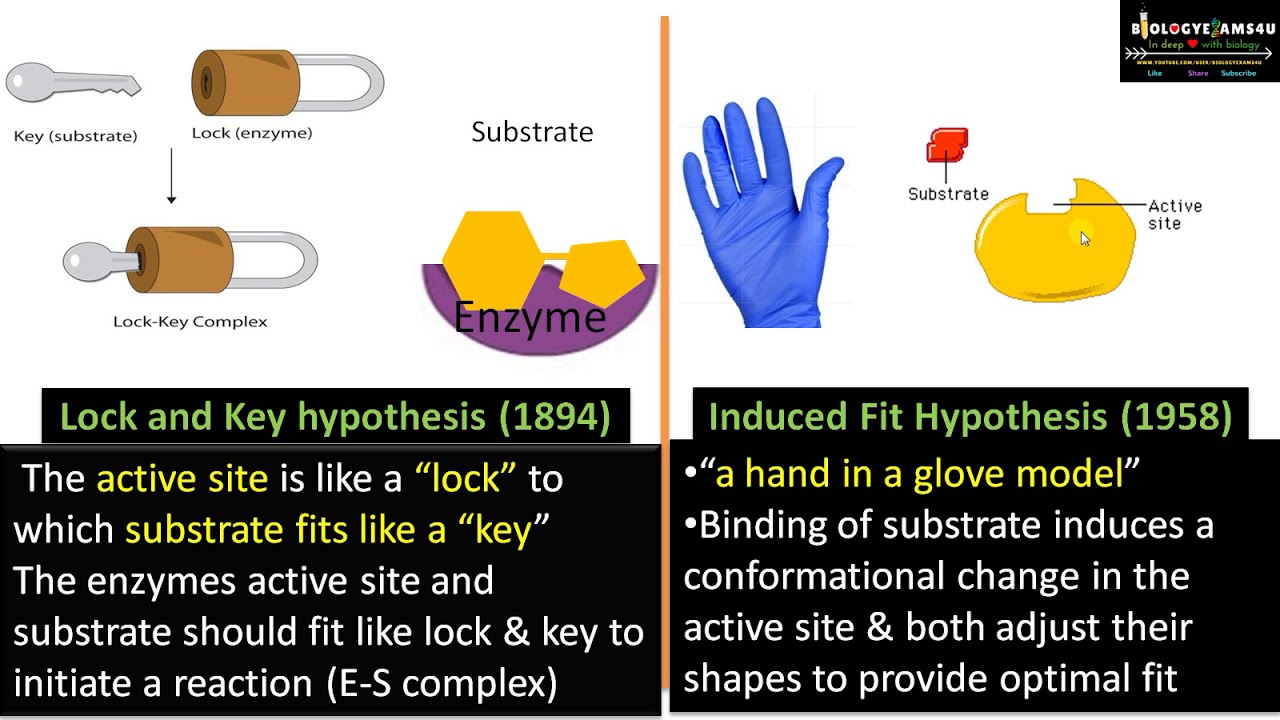
Difference Between Lock And Key Hypothesis And Induced Fit Hypothesis Choice Questions Biology Notes Lock And Key

Microbiology Notes On Instagram Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms Bacteria Can Resist The Action Of Microbiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Antibiotic

Pin By Tara Bear On Places To Visit Mindfulness Activities Immune Response Nasal Cavity

Mitochondria Structure And Function With Diagram Mitochondria Structure And Function Oxidative Phosphorylation

Protein Purification And Analysis Solubility Of Proteins Important For Purification 60 80 Soluble 20 40 Membr Analysis Fluorescence Spectroscopy Solubility

Mechanism Of Enzyme Action Biochemical Chemical Bond Enzymes

Mechanism Of Enzyme Action Enzymes Peptide Bond Active Site

Energy Released Invested Investing Chemistry Energy

What Is Enzyme In Biology Structure Location And Function Biology Enzymes Life Science

Lock And Key Model Is Used To Describe The Mechanism Of Enzyme Action This Model Was First Proposed By German Chemist Emil Fisher In 2021 Biology Lesson Video Lessons

Dehydration Synthesis Hydrolysis Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Education Chemistry Worksheets

Plant Vs Animal Cell Venn Diagram Plant And Animal Cells Animal Cell Venn Diagram


Comments
Post a Comment